 |
| Hybrid Sodium-Ion Batteries: Transforming Energy Storage [Image Source: KAIST] |
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have achieved a significant milestone in energy storage technology with the development of a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery. This breakthrough holds immense promise for revolutionizing the energy storage industry, offering a compelling alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Abundance and Accessibility of Sodium:
- Sodium, being over 500 times more abundant than lithium, emerges as a cost-effective and readily available alternative.
- Previous limitations of sodium-ion batteries, including lower power output and longer charging times, necessitated advancements in their performance.
KAIST's Hybrid Sodium-Ion Battery:
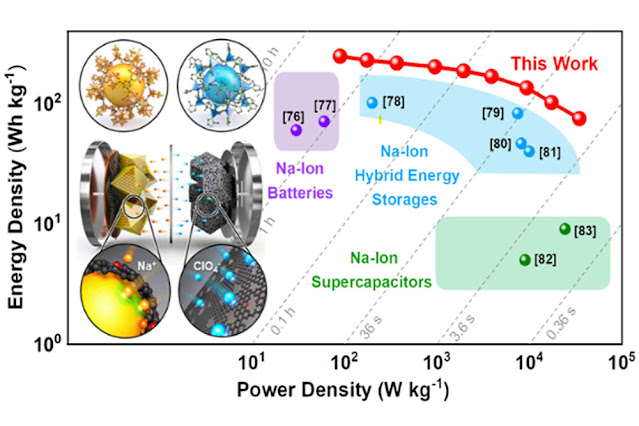
- Developed by Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team, this battery integrates anode materials from batteries with cathodes akin to supercapacitors.
- It achieves remarkable storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates, addressing previous shortcomings effectively.
Key Innovations:
- Utilization of distinct metal-organic frameworks optimized the synthesis of hybrid batteries.
- Anode material improvements include fine active materials within porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks.
- Synthesis of high-capacity cathode material and optimization of energy storage rate balance between electrodes contribute to enhanced performance.
Performance and Applications:
- The assembled full cell surpasses commercial lithium-ion batteries in energy density while exhibiting characteristics of supercapacitors in power density.
- Rapid charging capabilities with energy density reaching 247 Wh/kg and power density of 34,748 W/kg open doors for diverse applications across electronics, electric vehicles, and aerospace technologies.
Significance and Future Outlook:
- This breakthrough overcomes current limitations in energy storage systems, positioning sodium-ion batteries as a viable next-generation alternative.
- Anticipated to meet the escalating demand for low-cost, high-performance electrochemical energy storage devices, further research and development are crucial for scaling up and commercializing the technology.
